Understanding the PCB in Ultrasonic Cleaning Machines: Function, Design, and Optimization
Browse Volume:31 Classify:Support

Ultrasonic cleaning machines have revolutionized the way delicate and complex objects are cleaned. These machines use high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic cavitation bubbles in a cleaning solution, which effectively remove contaminants from surfaces. At the heart of this sophisticated technology lies the printed circuit board (PCB), which controls and powers the ultrasonic transducers. A well-designed PCB ensures efficiency, reliability, and performance, making it a crucial component of ultrasonic cleaning systems.
The Role of the PCB in an Ultrasonic Cleaning Machine
The PCB in an ultrasonic cleaning machine serves multiple essential functions. It acts as the control center, managing power distribution, frequency generation, and system feedback mechanisms. The primary role of the PCB includes:
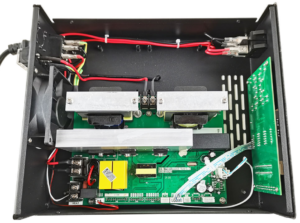
- Power Management: The PCB regulates electrical power and ensures that the ultrasonic transducers receive the correct voltage and current to generate high-frequency waves.
- Frequency Control: Ultrasonic cleaning relies on precise frequency generation. The PCB contains oscillators and microcontrollers that fine-tune these frequencies for optimal cleaning efficiency.
- Temperature and Safety Regulation: Many ultrasonic cleaners integrate heating elements, and the PCB ensures temperature stability while preventing overheating.
- User Interface Integration: Advanced ultrasonic cleaners feature digital displays and programmable settings, all managed through the PCB.
A malfunctioning PCB can lead to ineffective cleaning, inconsistent performance, or complete failure of the machine. Therefore, understanding the structure and function of this component is crucial.
Key Components of the PCB in Ultrasonic Cleaners
The PCB of an ultrasonic cleaning machine comprises several critical components that work together to ensure the system functions properly. Some of the most important elements include:

- Microcontroller Unit (MCU): Acts as the brain of the system, processing commands and executing programmed functions.
- Oscillator Circuit: Generates the high-frequency electrical signals required for ultrasonic transduction.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts AC power to regulated DC voltage suitable for the machine’s electronic components.
- MOSFETs and Transistors: Control and amplify the electrical signals delivered to the ultrasonic transducers.
- Feedback Sensors: Monitor and adjust the operation of the cleaning machine to maintain efficiency and stability.
Each of these elements must be carefully selected and integrated into the PCB layout to optimize the performance of the ultrasonic cleaning machine.
Design Considerations for an Efficient Ultrasonic Cleaning Machine PCB
Designing a PCB for an ultrasonic cleaning machine involves several crucial factors to ensure reliability, longevity, and effectiveness. Engineers must focus on the following aspects:
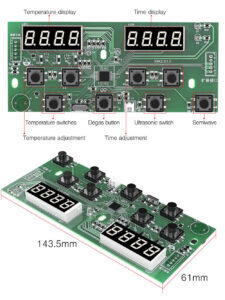
- Material Selection: PCBs are typically made from FR-4 material due to its durability and electrical insulation properties.
- Layer Configuration: Multi-layer PCBs are often used to enhance performance, with separate layers for power, control signals, and feedback systems.
- Thermal Management: Heat dissipation is essential, and components like heat sinks and cooling fans may be incorporated.
- Signal Integrity and Noise Reduction: Proper grounding techniques, shielding, and noise filters help maintain stable signal transmission and prevent interference.
- Component Placement and Soldering Quality: Ensuring optimal spacing and high-quality soldering prevents electrical shorts and enhances durability.
Engineers must also account for regulatory compliance, ensuring that the PCB meets safety standards and industry guidelines for electrical devices.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting PCB Failures in Ultrasonic Cleaners
Despite their reliability, PCBs in ultrasonic cleaning machines can experience failures due to various factors. Some common problems include:

- Power Fluctuations: Voltage irregularities can damage components, requiring voltage regulators or surge protection.
- Oscillator Circuit Malfunctions: If the frequency output is unstable, it may cause ineffective cleaning. Checking the crystal oscillator and capacitors can help.
- Overheating and Burnt Components: Poor heat management can lead to PCB failure, necessitating improved ventilation or heat dissipation solutions.
- Loose Connections or Corrosion: Moisture exposure may corrode PCB traces or loosen solder joints, requiring maintenance and protective coatings.
- Microcontroller Failures: A malfunctioning MCU can disrupt the entire system, requiring firmware updates or replacement.
Regular maintenance and periodic inspections can help detect early signs of PCB issues, preventing costly repairs and downtime.
Future Trends and Innovations in Ultrasonic Cleaning Machine PCBs
As technology advances, PCBs in ultrasonic cleaning machines continue to evolve. Some key trends and innovations include:

- AI-Integrated Control Systems: Machine learning algorithms can optimize cleaning cycles based on object material and contamination levels.
- Wireless Connectivity and IoT Integration: Future ultrasonic cleaners may feature smart connectivity, allowing remote monitoring and control.
- Energy-Efficient PCB Designs: Efforts to reduce power consumption and enhance energy efficiency are driving new PCB design approaches.
- Improved Durability and Miniaturization: Advances in materials and fabrication techniques enable more compact and durable PCB designs.
These developments will further enhance the effectiveness and usability of ultrasonic cleaning machines across various industries.
Ultrasonic cleaning machines depend on high-quality PCBs to ensure precision, efficiency, and durability. Understanding the role, design considerations, and potential issues of these PCBs allows manufacturers and users to maximize the effectiveness of these devices. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated PCB designs that further enhance ultrasonic cleaning capabilities.
References
- Zhu, X., & Wang, L. (2023). Design Optimization of Ultrasonic Cleaning Machine PCBs for Improved Efficiency. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology, 18(3), 257-270.
- Smith, J. & Patel, R. (2022). Power Management in Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems: A PCB Perspective. International Journal of Electronics and Automation, 29(4), 123-136.
- Lee, K. et al. (2021). Thermal Regulation in High-Frequency PCBs for Industrial Applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 68(7), 4876-4885.
- Chen, H. (2020). Advancements in Ultrasonic Cleaning Technology: The Role of Modern PCB Design. Microelectronics Journal, 51(2), 90-102.
 GranboSonic
GranboSonic














