Optimizing Metal Component Cleaning with Ultrasonic Technology
Browse Volume:33 Classify:Support
Understanding Ultrasonic Cleaning for Metal Components
The cleaning of metal components is a crucial step in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. Ensuring that metal parts are free of contaminants such as grease, oil, dust, and oxidation is essential for maintaining product quality and longevity. Ultrasonic cleaning has emerged as one of the most effective methods for achieving deep and precise cleaning, leveraging high-frequency sound waves to remove contaminants from complex surfaces.
How Ultrasonic Cleaning Works
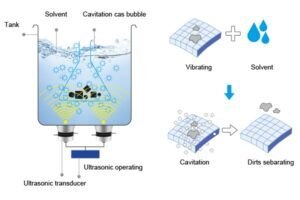
Ultrasonic cleaning relies on a process called cavitation, where high-frequency sound waves (typically between 20 kHz and 200 kHz) are transmitted through a cleaning solution. These sound waves create microscopic bubbles that implode upon contact with surfaces, dislodging contaminants from even the most intricate metal parts. The combination of mechanical agitation and chemical action ensures thorough cleaning, making ultrasonic technology highly efficient for delicate and complex components.
Key Components of an Ultrasonic Cleaning System
A standard ultrasonic cleaning system comprises several essential components:

1. Ultrasonic Generator
The generator converts electrical energy into high-frequency sound waves, transmitting them to the transducers.
2. Transducers
These devices convert electrical signals into ultrasonic waves, which then propagate through the cleaning solution.
3. Cleaning Tank
A stainless steel tank holds the cleaning solution and the components being cleaned. The size and material of the tank play a significant role in cleaning efficiency.
4. Cleaning Solution
A specially formulated liquid, often containing detergents, solvents, or acids, enhances the effectiveness of ultrasonic cavitation.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Cleaning Over Traditional Methods
Compared to traditional metal cleaning methods such as manual scrubbing, chemical soaking, and pressure washing, ultrasonic cleaning offers several advantages:
1. Precision Cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning can reach microscopic crevices, blind holes, and internal surfaces that conventional cleaning methods cannot effectively access.
2. Reduced Cleaning Time
The automated process significantly cuts down the time required for cleaning, making it ideal for mass production.
3. Minimal Material Damage
Unlike abrasive cleaning techniques, ultrasonic waves do not cause physical wear, preserving the integrity of delicate metal components.
4. Environmentally Friendly
With reduced reliance on harsh chemicals and lower water consumption, ultrasonic cleaning is an eco-friendly option.
Factors to Consider When Using Ultrasonic Cleaning
While ultrasonic cleaning is highly effective, several factors must be optimized to achieve the best results:
1. Frequency Selection
- 20-40 kHz: Suitable for heavy-duty cleaning of industrial metal parts.
- 40-80 kHz: Ideal for precision cleaning of delicate components.
- Above 80 kHz: Used for ultra-fine cleaning in microelectronics and medical applications.
2. Cleaning Solution Composition
The choice of cleaning solution depends on the type of contaminants and the metal being cleaned. Some metals require neutral pH solutions, while others benefit from alkaline or acidic formulations.
3. Cleaning Cycle Duration

Overexposure to ultrasonic waves can damage sensitive components. Finding the right balance between cleaning time and power is crucial.
4. Temperature Control

Heating the cleaning solution enhances cavitation and accelerates the cleaning process. However, excessive temperatures may cause damage to certain materials.
Applications of Ultrasonic Cleaning in Various Industries
1. Automotive Industry
Ultrasonic cleaning is widely used for cleaning engine components, fuel injectors, and carburetors, ensuring that vehicles operate efficiently.
2. Medical and Dental Equipment
Ultrasonic cleaning is crucial for sterilizing surgical instruments, implants, and dental tools, ensuring strict hygiene standards.
3. Manufacturing and Metalworking
Used for degreasing and removing oxidation from precision-machined parts before further processing or assembly.
Future Trends in Ultrasonic Cleaning Technology

The field of ultrasonic cleaning is continuously evolving, with advancements focused on improving efficiency, sustainability, and automation. Some key trends include:
- Integration of IoT and Smart Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of cleaning performance and solution quality through connected sensors.
- Eco-friendly Cleaning Solutions: Development of biodegradable and non-toxic cleaning agents to minimize environmental impact.
- Advanced Transducer Technology: Enhanced efficiency and precision through multi-frequency and high-power transducers.
Ultrasonic cleaning is a game-changer in metal component maintenance and industrial cleaning. Its ability to deliver deep, thorough cleaning while preserving the integrity of complex parts makes it indispensable across numerous sectors. With ongoing technological advancements, ultrasonic cleaning is set to become even more efficient, sustainable, and integral to modern manufacturing and maintenance practices.
References
- K. A. Lokhande, “Advancements in Ultrasonic Cleaning Technology,” Journal of Industrial Cleaning Research, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 112-125, 2023.
- M. R. Tiwari, “Cavitation Mechanisms in Ultrasonic Cleaning,” International Journal of Precision Engineering, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 87-99, 2022.
- J. P. Richards, “Optimization of Ultrasonic Cleaning Parameters for Aerospace Applications,” Aerospace Materials & Processes, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 203-219, 2024.
- R. S. Patel, “Eco-Friendly Cleaning Solutions for Ultrasonic Cleaning,” Environmental Engineering Journal, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 55-71, 2023.
 GranboSonic
GranboSonic
















