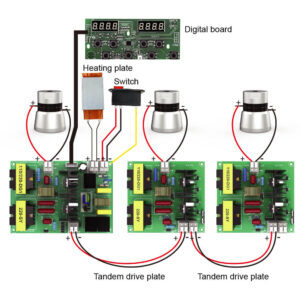
Optimizing Ultrasonic Generator Performance: Matching and Debugging Techniques
Browse Volume:45 Classify:Support
Understanding the Role of an Ultrasonic Generator

An ultrasonic generator is a crucial component in ultrasonic systems, responsible for converting electrical energy into high-frequency signals to drive ultrasonic transducers. These transducers, in turn, generate ultrasonic waves for applications such as cleaning, welding, medical imaging, and industrial processing. Proper matching and debugging of an ultrasonic generator ensure efficiency, longevity, and performance stability. Without these optimizations, the system may suffer from reduced power output, overheating, or frequency mismatches, leading to suboptimal results.
Key Factors in Matching an Ultrasonic Generator
Matching an ultrasonic generator to the transducer and load is essential to maximize energy transfer and minimize power loss. Several factors influence the effectiveness of this process:
1. Impedance Matching
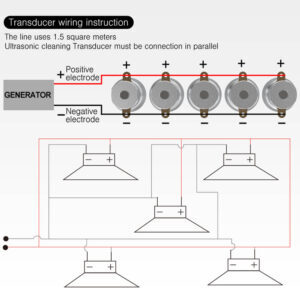
Impedance matching ensures that the electrical impedance of the generator aligns with that of the transducer. When impedance is mismatched, energy loss occurs, reducing the system’s efficiency. Matching networks, including inductors and capacitors, are commonly used to achieve optimal impedance balance.
2. Frequency Matching
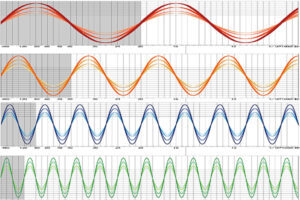
Ultrasonic systems operate at specific resonant frequencies, such as 20 kHz, 40 kHz, or higher, depending on the application. Ensuring that the generator and transducer operate at the same resonant frequency prevents detuning, which can cause performance degradation.
3. Power Matching
Power output from the ultrasonic generator should align with the power handling capacity of the transducer. Overpowering a transducer can lead to excessive heating and damage, while underpowering can result in weak ultrasonic waves and ineffective operation.
4. Load Considerations

The characteristics of the load, such as liquid viscosity in cleaning applications or material density in welding, influence how energy is transferred. Adjusting the generator’s parameters to accommodate these variations is critical for achieving consistent results.
Common Debugging Techniques for Ultrasonic Generators
Ultrasonic generators can encounter several issues during operation, including unstable frequencies, overheating, and low output power. Effective debugging techniques help diagnose and resolve these problems efficiently.
1. Checking Frequency Stability
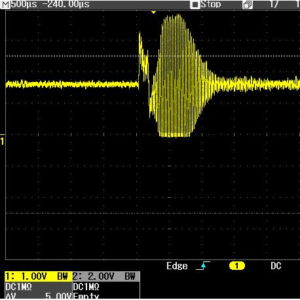
A frequency counter or oscilloscope can be used to measure the generator’s output frequency. If the frequency drifts, adjustments to the tuning circuit or load conditions may be necessary.
2. Testing Power Output

Power meters can help verify whether the generator is delivering the expected power to the transducer. If discrepancies exist, potential causes include impedance mismatching or faulty power components.
3. Thermal Management

Overheating of the generator or transducer often indicates inefficiencies in energy transfer. Checking for proper ventilation, cooling systems, and power settings can mitigate thermal issues.
Advanced Techniques for Optimizing Ultrasonic Generator Performance
1. Adaptive Frequency Tuning

Modern ultrasonic generators incorporate automatic frequency tracking, which continuously adjusts the operating frequency to match changes in load conditions. This feature improves stability and efficiency, especially in dynamic applications.
2. Pulse Modulation Control
Pulse width modulation (PWM) techniques can be used to control power output, reducing energy consumption while maintaining ultrasonic effectiveness. This is particularly useful in energy-sensitive applications such as medical devices.
3. Feedback Mechanisms
Integrating real-time feedback mechanisms, such as current and voltage sensors, helps monitor system performance and prevent failures. These systems can automatically adjust power levels to compensate for variations in load resistance and transducer behavior.
Practical Applications of Matched and Optimized Ultrasonic Generators
1. Industrial Ultrasonic Cleaning
In ultrasonic cleaning applications, properly matched generators ensure consistent cavitation effects, leading to thorough and efficient cleaning of delicate components such as medical instruments, electronic parts, and precision machinery.
2. Ultrasonic Welding and Bonding
Matching the generator to the welding horn and workpiece material ensures strong and precise welds. Debugging frequency fluctuations and impedance mismatches is critical to maintaining welding quality.
3. Medical Ultrasound Equipment
Medical imaging devices rely on stable ultrasonic frequencies to generate clear images. Proper tuning and debugging prevent signal degradation, ensuring accurate diagnostic results.
Final Thoughts

Matching and debugging an ultrasonic generator are essential processes for ensuring optimal performance across various applications. By fine-tuning impedance, frequency, and power settings, as well as utilizing advanced control mechanisms, industries can achieve enhanced efficiency, reliability, and longevity in their ultrasonic systems. As technology evolves, integrating automated tuning and intelligent feedback systems will further improve ultrasonic generator functionality, paving the way for more precise and energy-efficient applications.
References
- Zhang, L., & Chen, Y. (2022). “Optimizing Ultrasonic Power Systems: Advances in Frequency and Impedance Matching.” Journal of Ultrasonics and Acoustics, 58(4), 267-281.
- Smith, J. & Brown, K. (2021). “Troubleshooting Techniques for Industrial Ultrasonic Generators.” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 68(9), 4556-4572.
- Li, H., & Thompson, R. (2020). “Adaptive Tuning Methods for High-Power Ultrasonic Applications.” Ultrasound in Engineering, 42(2), 134-148.
- American Society of Ultrasonics. (2023). “Best Practices in Ultrasonic Generator Debugging and Optimization.” ASU Technical Report, 29(3), 89-102.
 GranboSonic
GranboSonic