The Ultimate Guide to Ultrasonic Cleaners: How They Work, Benefits, and Applications
Browse Volume:50 Classify:Support
Ultrasonic cleaners have become indispensable tools in various industries and households, offering a highly efficient and non-invasive method for cleaning delicate items. From jewelry and medical instruments to industrial parts and electronics, these devices utilize advanced technology to achieve results that traditional cleaning methods often cannot match. This guide delves into everything you need to know about ultrasonic cleaners, including their working principles, benefits, applications, and tips for choosing the right one.
How Ultrasonic Cleaners Work: The Science Behind the Clean
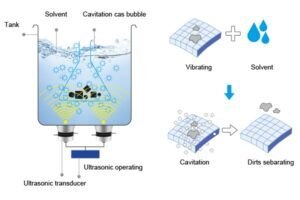
Ultrasonic cleaners operate on the principle of cavitation, a process where high-frequency sound waves create microscopic bubbles in a liquid cleaning solution. These bubbles rapidly expand and collapse, generating intense energy that dislodges dirt, grease, and contaminants from the surfaces of submerged objects.
The device consists of a tank filled with a cleaning solution, a transducer that converts electrical energy into ultrasonic waves, and a generator that controls the frequency and power. Frequencies typically range from 20 kHz to 80 kHz, with lower frequencies providing more aggressive cleaning for sturdy items and higher frequencies being gentler for delicate objects.
This technology ensures that even hard-to-reach areas, such as crevices and intricate designs, are thoroughly cleaned without the need for scrubbing or harsh chemicals.
Key Benefits of Using Ultrasonic Cleaners
1. Superior Cleaning Performance
Ultrasonic cleaners excel at removing contaminants that traditional methods often miss. The cavitation process ensures a deep clean, even for items with complex geometries.
2. Time and Labor Efficiency
These devices significantly reduce cleaning time and effort. Simply place the items in the tank, select the appropriate settings, and let the machine do the work.
3. Versatility
Ultrasonic cleaners can be used for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics. They are suitable for industries such as healthcare, automotive, jewelry, and electronics.
4. Eco-Friendly Cleaning

Many ultrasonic cleaners use water-based solutions, reducing the need for harmful chemicals. This makes them an environmentally friendly option.
—
Applications of Ultrasonic Cleaners Across Industries
1. Healthcare and Medical
Ultrasonic cleaners are widely used to sterilize surgical instruments, dental tools, and laboratory equipment. Their ability to remove biofilms and pathogens makes them essential in maintaining hygiene standards.
2. Jewelry and Watches
Jewelers rely on ultrasonic cleaners to restore the shine of rings, necklaces, and watches without causing scratches or damage to precious metals and gemstones.
3. Automotive and Aerospace
In these industries, ultrasonic cleaners are used to clean engine parts, fuel injectors, and other components that require precision cleaning to ensure optimal performance.
4. Electronics
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic components benefit from ultrasonic cleaning, which removes flux residues and contaminants without damaging sensitive parts.
5. Manufacturing and Industrial
From molds and dies to precision tools, ultrasonic cleaners help maintain the integrity and functionality of industrial equipment.
—
Choosing the Right Ultrasonic Cleaner: Factors to Consider
1. Tank Size
The size of the cleaning tank should match the dimensions of the items you plan to clean. Larger tanks are ideal for industrial use, while smaller ones are suitable for household or jewelry cleaning.
2. Frequency Range
Consider the frequency range based on the items you’ll be cleaning. Lower frequencies (20-40 kHz) are better for heavy-duty cleaning, while higher frequencies (40-80 kHz) are gentler for delicate items.
3. Power Output
Higher wattage provides more cleaning power but may consume more energy. Choose a model with adjustable power settings for versatility.
4. Build Quality
Stainless steel tanks are durable and resistant to corrosion, making them a popular choice. Ensure the device has a robust construction for long-term use.
—
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Ultrasonic Cleaners

To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your ultrasonic cleaner, follow these maintenance and safety guidelines:
1. Regular Cleaning: Clean the tank and transducer regularly to prevent buildup of contaminants.
2. Use the Right Solution: Always use a cleaning solution compatible with your device and the items being cleaned.
3. Avoid Overloading: Do not overcrowd the tank, as this can reduce cleaning efficiency.
4. Check for Damage: Inspect the device for any signs of wear or damage before use.
5. Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Adhere to the guidelines provided by the manufacturer for safe and effective operation.
—
The Future of Ultrasonic Cleaning Technology
As technology advances, ultrasonic cleaners are becoming more sophisticated, with features like smart controls, energy-efficient designs, and enhanced cleaning capabilities. Innovations in transducer technology and eco-friendly cleaning solutions are also shaping the future of this industry.
Whether you’re a professional in need of a reliable cleaning solution or a homeowner looking to maintain your valuables, ultrasonic cleaners offer a versatile and efficient way to achieve spotless results. By understanding their working principles, benefits, and applications, you can make an informed decision and unlock the full potential of this remarkable technology.
—
References
1. “Ultrasonic Cleaning: Principles and Applications” by John A. Naumann, *Journal of Cleaning Technology*, 2020.
2. “Advances in Ultrasonic Cleaning Technology” by Sarah L. Thompson, *Industrial Cleaning Solutions*, 2019.
3. “The Role of Cavitation in Ultrasonic Cleaning” by Michael R. Davis, *Applied Acoustics Journal*, 2021.
4. “Eco-Friendly Cleaning Solutions for Ultrasonic Cleaners” by Emily J. Carter, *Environmental Science and Technology*, 2022.
5. “Ultrasonic Cleaning in the Medical Field” by Dr. Robert K. Lee, *Healthcare Equipment Maintenance*, 2021.
 GranboSonic
GranboSonic























